

The mLink Environmental Sensor Module combines multiple precision sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, ambient light, and white light levels. Designed for easy integration with microcontrollers via mLink I²C interface, this module provides accurate and reliable environmental data for weather stations, automation systems, indoor climate monitoring, and more.

mLink I²C Interface
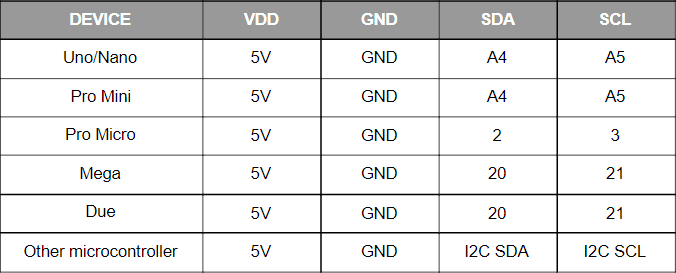
- Microcontroller Compatibility: Works with any microcontroller or development board with a standard I²C interface
- Expandable System: Seamlessly daisy-chain with other mLink modules (e.g., displays, relays, input devices) using a single I²C connection
- Unified Library: A single Arduino library or Raspberry Pi module with a tiny memory footprint enables control of all connected mLink modules.
Arduino & Raspberry Pi Support
- Arduino: An Arduino library is available via GitHub, PlatformIO, or directly from out support forum.
- Raspberry Pi: A Raspberry Pi Compatible Python module is available via PyPi for easy installation.s
- Resources Provided: Code example(s) and documentation are available to help you get started quickly
Use Cases
- Smart weather stations
- Environmental monitoring
- Greenhouse automation
- Indoor lighting control based on ambient conditions
- Climate-aware IoT systems
Module Specifications:
Product code: HCMODU0265 Supply Voltage: 5V via mLink header (3.3V via solder pad) Supply current: ~700uA (idle), ~170uA (sleep) Temp sensor range: -40 to 85oC Temp sensor resolution: 0.01oC Hum sensor range: 0 to 100%RH Hum sensor resolution: 0.024%RH Pressure sensor range: 300 to 1100hPa / mBar Pressure sensor resolution: 0.01hPa / mBar Light sensor range: 0 to 35232lx Light sensor resolution: 0.54lx I²C Interface speed: 400kbits/s (fast mode) I²C default address (HEX): 0x61 Maximum number of modules: 5 with pullups fitted, 112 with pullups removed* Module dimensions: 27mm x 21mm x 11.5mm (excluding headers) *Note: Do not exceed 5 mLink modules in series with pullups fitted to all modules. For chaining more modules, see the mLink pullup configuration guide.


- /* FILE: mLink_Env_Sensor_Example.ino
- DATE: 23/06/25
- VERSION: 1.0
- AUTHOR: Andrew Davies
- This sketch uses the mLink library to repeatedly read the
- sensors of the mLink environmental sensor module and output
- the result to the serial monitor.
- Please see Licence.txt in the library folder for terms of use.
- */
- #include "mLink.h" // Include the library
- mLink mLink; // Create an instance of the library
- #define I2C_ADD 0x61 // Default I2C address
- void setup()
- {
- Serial.begin(9600);
- mLink.init(); // Initialise the library
- }
- void loop()
- {
- mLink.wake(I2C_ADD); // Wake device
- mLink.envSens_Trigger(I2C_ADD); // Trigger a measurement
- while(mLink.busy(I2C_ADD)); // Wait until done
- float tmp = mLink.envSens_Temp(I2C_ADD); // Get new temperature (oC)
- float hum = mLink.envSens_Hum(I2C_ADD); // Get new humidity (%RH)
- float prs = mLink.envSens_Pres(I2C_ADD); // Get new pressure (mbar/hPa)
- float amb = mLink.envSens_Amb(I2C_ADD); // Get new ambient light (lux)
- float wht = mLink.envSens_Wht(I2C_ADD); // Get new white light (lux)
- mLink.sleep(I2C_ADD); // Go back to sleep
- // Print the results
- Serial.print("Temp:\t"); Serial.println(tmp);
- Serial.print("Hum:\t"); Serial.println(hum);
- Serial.print("Pres:\t"); Serial.println(prs);
- Serial.print("Amb:\t"); Serial.println(amb);
- Serial.print("White:\t"); Serial.println(wht);
- Serial.println("");
- delay(2000);
- }


When connecting to a Raspberry Pi the mLink modules I2C pullup resistors should be removed. See the 'Removing the modules I2C pullup resistors' section below for more information.
- # mLink environmental sensor example
- # This example demonstrates how to read the various sensors of the
- # mLink Environmental sensor module.
- #
- # To use this script you will need to have the mLink module installed.
- # Please see library forum thread for more information:
- #
- # https://forum.hobbycomponents.com/viewtopic.php?f=131&t=3135
- from mLink import mLink # Import the mLink module
- import time
- ml = mLink.mLink(1) # Create an instance of the module
- I2C_ADD = 0x61 # Default I2C address is 0x61
- while 1:
- ml.envSens_Trigger(I2C_ADD)
- while (ml.busy(I2C_ADD)): # Wait for data to be transmitted
- continue
- tmp = ml.envSens_Temp(I2C_ADD) # Get temperature in oC
- hum = ml.envSens_Hum(I2C_ADD) # Get humidity in %RH
- prs = ml.envSens_Pres(I2C_ADD) # Get pressure in mBar/hPa
- amb = ml.envSens_Amb(I2C_ADD) # Get ambient light in lux
- wht = ml.envSens_Wht(I2C_ADD) # Get white light in lux
- print("Tmp =", tmp); # Print the results
- print("Hum =", hum);
- print("Prs =", prs);
- print("Amb =", amb);
- print("Wht =", wht, "\n");
- time.sleep(2) # Wait a little before reading again

Dimensions:

Factory Reset:
Should you wish to restore the module back to its factory default configuration, this can be done by manually forcing a factory reset. All mLink modules include a set of pads labelled clear:

To perform a factory reset carefully link the two pads together with a piece of wire or with something conductive such as a paperclip. Whilst linked, connect power to the module via the VCC and GND connections. Wait a few seconds and then remove the short from the pads. The module's settings, including its I2C address, should now be restored back to factory defaults.
Removing I2C pullups:
If your development board already has pullups for its I2C interface fitted, or you wish to connect more than 5 mLink boards to the same I2C interface, then you can remove the pullups for the additional boards by cutting the tracks between the solder pads shown below.


mLink Arduino library
viewtopic.php?f=58&t=3001
Please note that you will need at least V2.3.0 (25 Jun 2025) of the library to support this module. If you have an older version already installed please update it to the latest version.
mLink Raspberry Pi Python module
The mLink python module can be installed with the following terminal command:
- pip install hc-mlink
Alternatively the library can be manually installed by downloading it from the forum and unzipping it to your project folder. See the Python module forum thread for more information and download link:
viewtopic.php?f=131&t=3062&p=8592#p8592
Please note that in some cases there may be additional configuration required. If you have issues getting your Raspberry Pi to communicate with the mLink module then please see the Python module forum thread here: viewtopic.php?f=131&t=3062
mLink Specifications and Register Map
https://hobbycomponents.com/downloads/m ... er_Map.pdf
Libraries, example code, and diagrams are provided as an additional free service by Hobby Components and are not sold as part of this product. We do not provide any guarantees or warranties as to their accuracy or fitness for purpose.